Chiral β-arylamines exist in numerous biologically interesting natural products and therapeutic agents. For examples, such moieties commonly exist in a series of naphthylisoquinoline alkaloids such as Michellamine B and Korupensamine A.They also serve as pivital structural units for many active pharmaceutical ingredients such as MDA,tamsulosin, selegiline, arformoterol, rotigotine,and silodosin. Development of efficient asymmetric synthetic methods of chiral β-arylamines has thus become a subject of significant interests.One of the most attractive methods is asymmetric hydrogenation of readily accessible (E)-β-arylenamides, which has proven to be difficult with currently known catalysts.
A novel C2-symmetric bisphosphorus ligand-WingPhos (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 4235-4238) with a deep chiral pocket has been recently developed from the research group of Professor Wenjun Tang in State Key Laboratory of Bioorganic & Natural Products Chemistry of Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Its rhodium complex has shown high efficiency (up to 99% ee, up to 10,000 s/c ratio)in asymmetric hydrogenation of (E)-β-aryl-N-acetyl enamides, cyclic β-arylenamides, and heterocyclic β-arylenamides. A series of important chiral intermediates such as chiral β-arylisopropylamines, 2-aminotetralines, and 3-aminochromans can thus be efficiently synthesized. The methodology is potentially practical for the syntheses of several key chiral intermediates of therapeutic agents and natural products. The project is financially supported by the “Thousand Plan” Youth program, the National Natural Science Foundations of China, and Chinese Academy of Sciences.
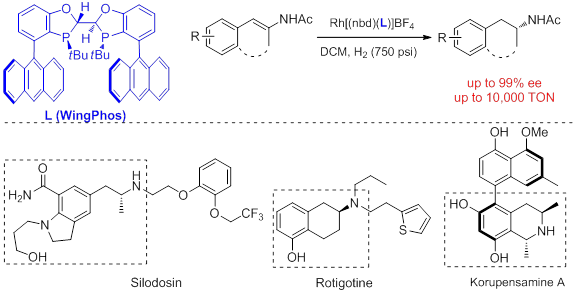
WingPhos shown high efficiency in asymmetric hydrogenation. (Imaged by TANG wenjun @SIOC) |


