Researchers at Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences have developed a catalytic system that directly installs the trifluoromethyl group onto arenes. The new reaction uses simple and abundant trifluoroacetic acid as the trifluoromethylating agent, and offers a milder alternative to the existing strategies (Figure 1).
Published on August 5 in the journal Cell Reports Physical Science, the reported transformation is the first to successfully use trifluoroacetic and related acids as trifluoromethyl, chlorodifluoromethyl, and perfluoroalkyl radical sources with visible light irradiation.
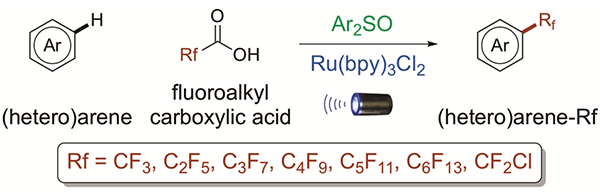
Figure 1. Trifluoromethylation, Chlorodifluoromethylation and Perfluoroalkylation of Arenes
Fluorinated drugs have better membrane permeability and increased bioavailability compared with their non-fluorinated analogues because of the changes in the physical and chemical properties. Trifluoromethyl group is one of the privileged moieties in modern drug discovery. Among the top 200 small molecule pharmaceuticals by retail sales in 2018, there were 15 drugs containing at least one trifluoromethyl group, mostly (80%) on their aryl or heteroaryl scaffolds. Therefore, simple methodologies for the incorporation of trifluoromethyl group into arenes and heteroarenes are highly desirable.
Trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) is among the most attractive trifluoromethylation reagents with respect of its low prices, ease of handling, and availability in large quantities. However, because of its exceedingly high oxidation potential, harsh conditions are required for the direct oxidation of TFA to the trifluoroacetate radical, which after prompt CO2 extrusion affords the desired CF3 radical (Figure 2A).
The combination of photoredox catalysis and a diaryl sulfoxide provides a platform for the facile generation of CF3 radical from trifluoroacetic acid under mild conditions (Figure 2B). The resultant CF3 radical would then add to the (hetero)arene substrate, followed by an oxidative re-aromatization process to afford the trifluoromethylated (hetero)arene product.
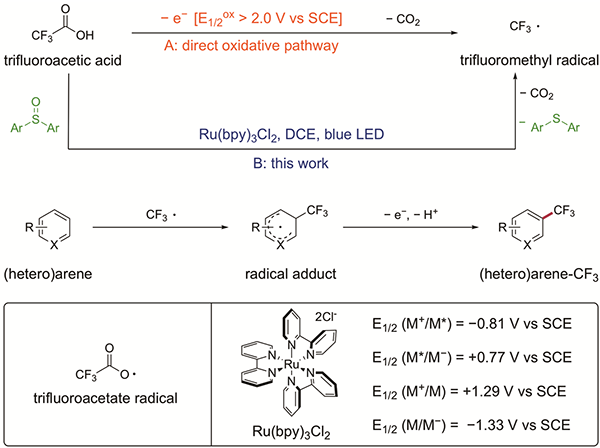
Figure 2. Working Hypothesis for the Trifluoromethylation
This protocol is applicable for chlorodifluoromethylation and perfluoroalkylation as well. And a diverse array of arenes and heteroarenes were successfully transformed into valued fluoroalkylated compounds.
We anticipate this visible light-promoted C–H fluoroalkylation method will find broad application, said Professor Jian Jin who led the project.
This work was supported by Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (19ZR1468700), Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry, and Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Read the full article here:
Yin, D.; Su, D.; Jin, J. “Photoredox Catalytic Trifluoromethylation and Perfluoroalkylation of Arenes Using Trifluoroacetic and Related Carboxylic Acids.” Cell Reports Physical Science 2020, DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrp.2020.100141.
Jin Jian
Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Ling Ling Road 345 Shanghai 200032 China
Tel: 0086-21-54925025
Email: jjin@sioc.ac.cn


